Procedures¶
Procedures are custom pieces of AMIScript for consistently manipulating tables. They are a useful way to reuse code and make projects easier to maintain.
CREATE PROCEDURE¶
This command allows you to create stored procedures that can be called via amiscript to execute a sequence of statements and return a value. Arguments can be supplied when calling the stored procedure (see CALL PROCEDURE):
procedure_name- name of the procedure to be created, each procedure's name must be unique within the database
Logging options:
off(default): no logging.on: logs the time when the timer is called and when it completes.verbose: equivalent of using show_plan=ON in AMIDB. Logs the time that a timer starts and finishes and also each query step.
Example¶
In this example lets assume we have a table MyTable(id int,price double). We will make a simple procedure that inserts a row into that table and deletes any other rows with an equal or lesser price. (See CALL PROCEDURE clause for example of calling this procedure)
CALL¶
This command allows you to execute stored procedures, typically declared using the CREATE PROCEDURE clause. When calling procedures you must supply the appropriate arguments expected for the declared procedure.
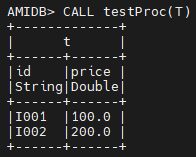
Example¶
In this example we will call the procedure declared in the CREATE PROCEDURE clause.
DROP PROCEDURE¶
Example¶
This example will drop the procedure MyProcedure from the database
String Templating¶
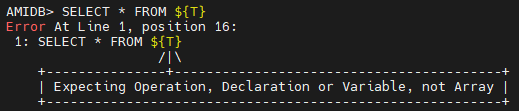
String templating can be complex with procedures, this section will go through an example of how to use string templating. First let us create a simple table and add 4 values to it:
Running this select query:
Gives us the following table:
Now let's create a string and assign A to it:
Try running the following script:
This produces an error as string_template=off.
Let's set string_template=on. Note we find string_template under the setlocal command:
To set this to 'on' run the following:
Try running the following script again:
This will now output table A.
Let's roll back and set string_template=off. This time we will create the following PROCEDURE:
and then call the procedure as such:
List of System Procedures¶
This section will cover most of the procedures included in AMI by default, however the following procedures are covered in the Center Replication page:
-
__ADD_CENTER -
__REMOVE_CENTER -
__ADD_REPLICATION -
__REMOVE_REPLICATION
__ADD_DATASOURCE¶
options: Refers to values under the Advanced section. Must be a comma-delimited list e.g.DISABLE_BIGDEC=true,URL_OVERRIDE=jdbc:mysql://serverUrl:1234/databaseNamerelayId: Refers to "Relay to Run on" under the Configuration section.permittedOverrides: Refers to the checkboxes under the Security section. Must be a comma delimited list. The available values are URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD, OPTIONS, RELAY e.g. to tick the URL and USERNAME checkboxes useURL,USERNAME.-
url: Refers to the URL that the datasource is hosted.- To connect to another AMI datasource, you will need to use the configured port corresponding to that instance's
ami.db.jdbc.portproperty (by default this is 3280). - E.g:
CALL __ADD_DATASOURCE("ami_datasource", "AMIDB", "some.host:1780", "demo", "demo123", null,null,null);
- To connect to another AMI datasource, you will need to use the configured port corresponding to that instance's
Supported Adapter Types¶
| Name | Alias (to be used in the procedure call) |
|---|---|
| AMI datasource | __AMI |
| Sybase IQ JDBC | SYBASE_IQ |
| Shell Command | SHELL |
| AMIDB | AMIDB |
| MySQL JDBC | MYSQL |
| KDB | KDB |
| SSH Command | SSH |
| Redis | Redis |
| Fred | FRED |
| SQLServer JDBC | SQLSERVER |
| Oracle JDBC | ORACLE |
| Sybase JDBC | SYBASE |
| RestAPI | RESTAPI |
| Postgres JDBC | POSTGRES |
| Flat File Reader | FLAT_FILE |
| Generic JDBC | GENERIC_JDBC |
| IMB DB2 | IMBDB2 |
| SQLITE JDBC | SQLITE |
| OneTick | ONETICK |
| Quandl | QUANDL |
__REMOVE_DATASOURCE¶
This procedure removes the specified datasource. Use show datasources to see a list of available datasources.
__RESET_TIMER_STATS¶
This procedure clears NextRunTime. Optionally clears ExecutedCount, MillisSpent, and AvgMillisSpent if ExecutedStats is set to true, and optionally clears ErrorCounts if ErrorStats is set to true. Use show timers to see a list of available timers.
__RESET_TRIGGER_STATS¶
This procedure will reset ExecutedCount, MillisSpent, AvgMillisSpent, ErrorsCount, ReturnedFalseCount for a particular trigger. Use show triggers to see information for all triggers.
__SCHEDULE_TIMER¶
This procedure schedules the timer to run after the specified number of milliseconds passes. For instance, call __SCHEDULE_TIMER("mytimer", 5000) means mytimer will start running after 5000 milliseconds, or 5 seconds.
__SHOW_TIMER_ERROR¶
This procedure shows you the last error the specified timer encountered in a table format.
__SHOW_TRIGGER_ERROR¶
This procedure shows you the last error the specified trigger encountered in a table format.